爱星物联平台提供智能场景功能,该功能可以将多设备组合在一次进行一键执行,也可以根据天气、定时、监听设备变化等方式进行自动化执行,今天我们将深入代码看看这个智能场景功能吧
智能场景的使用说明
推荐场景的配置
开放平台提供推荐场景的配置,根据平台产品预设一些常用的场景,帮助用户快速添加场景;

APP推荐场景部分截图
智能场景功能介绍
一键执行
一键执行是去掉条件判断的智能场景,APP配置好执行规则,用户点击执行按钮,场景服务按照设定的规则和顺序执行;如:
- 一键执行任务1:A设备开启、B设备关闭、延时等待1分钟之后,在将A设备设置为5档;
- 一键执行任务2:一键将家里所有的智能灯打开/关闭;
触发一键执行之后,执行任务为异步操作的,因为用户可以设定设备状态变化、延时执行,这些任务的完成时间不确定,所以需要APP在执行弹框页面,调接口轮询执行结果;
func (s *SceneIntelligenceSvc) OneKeyExec(req *proto.SceneIntelligencePrimarykey) (int64, error) {
//查询智能场景详情
retData, err := s.FindByIdSceneIntelligence(&proto.SceneIntelligenceFilter{
Id: req.Id,
})
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
taskSvc := SceneIntelligenceTaskSvc{Ctx: s.Ctx}
//查询智能场景任务列表
taskRet, _, err := taskSvc.GetListSceneIntelligenceTask(&proto.SceneIntelligenceTaskListRequest{
Query: &proto.SceneIntelligenceTask{
IntelligenceId: req.Id,
},
})
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
if retData != nil && taskRet != nil && len(taskRet) > 0 {
retData.SceneIntelligenceTask = taskRet
resultId := iotutil.GetNextSeqInt64()
go func() {
defer iotutil.PanicHandler()
//按照步骤执行任务
executor := scene_executor.SceneIntelligenceExecutor{}
executor.ExecuteTask(retData, resultId)
}()
return resultId, nil
} else {
return 0, errors.New("查询智能场景失败")
}
}
自动化执行
自动化智能场景架构如下:

场景服务中根据设备状态变化、定时器和天气变化对条件进行分组管理,条件管理器将通过消息订阅、定时器等方式对条件进行监听;例如: A场景中的条件是B设备打开时去关闭C设备,那么框架会将B设备打开的条件注册到设备条件管理器中,并订阅该设备的设备状态变化,如果检测到B设备开关变化为开启,则使用规则引擎组件触发条件检查服务,因为我们的条件并非只有一个,他可以是若干个条件的组合,所以这里还需要多走了一层服务;
APP用户创建场景的时候,平台将根据用户的规则创建场景,如果存在天气条件还需要增加监听该用户所在城市的天气变化;
rule := scene_executor.IntelligenceRule{}
//创建场景规则任务
rule.CreateRule(iotutil.ToString(dbObj.Id), dbObj.Title)
if req.SceneIntelligenceCondition != nil {
//如果是天气,则增加该城市天气监听,如果已监听过了的城市将不会重复监听
for _, condition := range req.SceneIntelligenceCondition {
if iotconst.ConditionType(condition.ConditionType) == iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_WEATHER {
scene_executor.MonitorWeatherChange(condition.GetWeatherCity())
}
}
}
在CreateRule中将会根据条件类型注册到对应条件管理器,并创建对应的引擎规则,规则的Id为场景的ID,这样在场景执行的时候就可以通过场景Id触发规则执行;
for _, condition := range intellObj.SceneIntelligenceCondition {
conditionId := iotutil.ToString(condition.Id)
switch iotconst.ConditionType(condition.ConditionType) {
case iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_WEATHER:
//天气条件
obs := WeatherObserver{id: id, city: condition.WeatherCity, weatherType: condition.WeatherType, weatherCompare: condition.WeatherCompare, weatherValue: condition.WeatherValue}
weatherManagers.register(obs)
valscene.WeatherRuleBuilder.BuildRuleWithIncremental(genRuleAuto(id, desc, 10, conditionId))
c.ConditionExecutor(id, "")
case iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_SATACHANGE:
//设备状态变化
obs := DeviceObserver{id: id, did: condition.DeviceDid, funcKey: condition.DevicePropKey, funcValue: condition.DevicePropValue}
deviceManagers.register(obs)
valscene.DeviceRuleBuilder.BuildRuleWithIncremental(genRuleAuto(id, desc, 10, conditionId))
case iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_TIMER:
// 创建定时器
obs := TimerObserver{id: id, weekVal: condition.TimerWeeks, timeVal: condition.TimerValue, timezone: intellObj.Timezone, regionServerId: intellObj.RegionServerId}
timeManagers.register(obs)
valscene.TimerRuleBuilder.BuildRuleWithIncremental(genRuleAuto(id, desc, 10, conditionId))
}
}
// 这里看到我们每新增一个智能场景都会根据他的条件数量创建对应的规则引擎,引擎的Id为场景Id,之后触发场景运行则直接通过场景Id即可;
// valscene.WeatherRuleBuilder.BuildRuleWithIncremental
// valscene.DeviceRuleBuilder.BuildRuleWithIncremental
// valscene.TimerRuleBuilder.BuildRuleWithIncremental
条件管理器
设备条件管理器
// initSub 初始化设备状态变化
func (s *ObserverDeviceStatusItems) initSub() {
s.observerHasMap = sync.Map{}
go func() {
for {
select {
case job := <-DeviceChan:
s.notifyByDid(job.DeviceId, &job)
}
}
}()
}
// register 指定设备注册到设备条件管理器
func (s *ObserverDeviceStatusItems) register(o observerDevice) (bool, error) {
s.observerList = append(s.observerList, o)
s.observerHasMap.Store(o.getKey(), o)
return true, nil
}
// notifyByDid 检测设备状态上报,调用该方法判断设备状态是否发生变化,并发起场景执行逻辑
func (s *ObserverDeviceStatusItems) notifyByDid(did string, data *iotstruct.DeviceRedisData) {
if !s.check(did, data) {
//当前天气无变化
return
}
mapKey, _ := s.observerHasMap.Load(did)
if mapKey == nil {
return
}
go func() {
iotlogger.LogHelper.Infof("设备条件管理器 设备Id:%s", did)
ob := mapKey.(observerDevice)
ob.run(data)
}()
}
//run方法中检查状态变化,并调起规则引擎
func (w DeviceObserver) run(data *iotstruct.DeviceRedisData) bool {
if valscene.Gengine == nil {
return false
}
if valscene.DeviceRuleBuilder == nil {
return false
}
status := data.Data.(map[string]interface{})
v, ok := status[w.funcKey]
if ok && iotutil.ToString(v) == iotutil.ToString(w.funcValue) {
err := valscene.Gengine.ExecuteSelectedRules(valscene.DeviceRuleBuilder, []string{w.getRuleId()})
if err != nil {
return false
}
}
return true}
定时条件管理器
// 这是注册定时执行的定时器
func (s *ObserverTimerItems) register(o observerTimer) (bool, error) {
cronStr := s.generateCron(o)
if cronStr == "" {
return false, errors.New("执行表达式生成异常")
}
//创建定时器
entryId, err := cron2.CronCtx.AddFunc(cronStr, func() {
s.notify(o.getRuleId())
})
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
o.setEntryId(entryId)
s.observerHasMap.Store(o.getRuleId(), o)
return true, nil
}
//定时到,开始执行场景任务,这里通过的条件,在场景运行不会再次检查,但是会检查其它条件;
func (w TimerObserver) run() bool {
if valscene.Gengine == nil {
return false
}
if valscene.TimerRuleBuilder == nil {
return false
}
//当前任务为执行一次,还是重复执行
if w.weekVal == "" {
cron2.CronCtx.Remove(w.entryId)
}
err := valscene.Gengine.ExecuteSelectedRules(valscene.TimerRuleBuilder, []string{w.getRuleId()})
if err != nil {
return false
}
return true
}
天气条件管理器
// 初始化天气订阅
func (s *ObserverWeatherItems) initSub() {
go func() {
for {
select {
case job := <-WeatherChan:
iotlogger.LogHelper.Info("weather:", job)
s.notifyByCity(iotutil.ToString(job["city"]), job)
}
}
}()
}
// 注册天气条件
func (s *ObserverWeatherItems) register(o observer) (bool, error) {
if s.observerList == nil {
s.observerList = make([]observer, 0)
}
s.observerList = append(s.observerList, o)
return true, nil
}
//城市天气变化,通过有所与之相关的场景任务
func (s *ObserverWeatherItems) notifyByCity(city string, weather map[string]interface{}) {
if !s.check(city, weather) {
//当前天气无变化
return
}
//天气发送变化通知所有观察者
for _, o := range s.observerList {
if city == o.getKey() {
o.run(weather)
}
}
}
//天气变化了,找到所有该城市的场景,逐个执行,这里通过的条件,在场景运行不会再次检查,但是会检查其它条件;
func (w WeatherObserver) run(weather map[string]interface{}) bool {
if valscene.Gengine == nil {
return false
}
if valscene.WeatherRuleBuilder == nil {
return false
}
weatherKey := valscene.WeatherType[w.weatherType]
isPush := false
weatherType := iotconst.WeatherType(w.weatherType)
switch weatherType {
case iotconst.WEATHER_TYPE_WEATHER, iotconst.WEATHER_TYPE_SUN:
switch w.weatherCompare {
case 2: //等于
if v, ok := weather[weatherKey]; ok {
isPush = v == w.weatherValue
}
}
case iotconst.WEATHER_TYPE_TEMPERATURE, iotconst.WEATHER_TYPE_HUMIDITY, iotconst.WEATHER_TYPE_PM25, iotconst.WEATHER_TYPE_WINDSPEED:
if v, ok := weather[weatherKey]; ok {
val, err1 := iotutil.ToFloat64Err(w.weatherValue)
cVal, err2 := iotutil.ToFloat64Err(v)
if err1 == nil && err2 == nil {
return false
}
val = math.Round(val)
cVal = math.Round(cVal)
switch w.weatherCompare {
case 1: //小于
isPush = cVal < val
case 2: //等于
isPush = cVal == val
case 3: //大于
isPush = cVal > val
}
}
}
if isPush {
err := valscene.Gengine.ExecuteSelectedRules(valscene.WeatherRuleBuilder, []string{w.getRuleId()})
if err != nil {
return false
}
}
return true
}
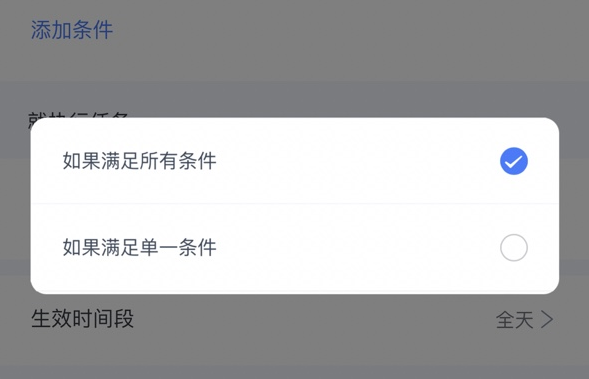
规则引擎的执行方法中,除了传入的条件不需要重复检查外,场景中其它条件还需要根据条件的真实情况进行判断,当然条件满足状态也是有失效的,不能昨天某个条件满足,到今天也还是满足的,所以每个添加都会进行缓存,缓存时间为若干分钟即可,然后根据场景的规则“全部条件满足” or “任意条件满足” 来判断是否需要检查其它条件,只有最终条件判断为true才会真实执行场景;
//其它条件判断逻辑
//省略..
for _, cond := range intellObj.SceneIntelligenceCondition {
//外部conditionId,代表该条件已经满足
if conditionId == iotutil.ToString(cond.Id) {
resultFlag = append(resultFlag, true)
continue
}
switch iotconst.ConditionType(cond.ConditionType) {
case iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_SATACHANGE:
resultFlag = append(resultFlag, u.DeviceStatusCheck(intellObj, cond, redisSaveQueue))
case iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_TIMER:
isSuc := false isSuc, _ = u.DelayedCheck(intellObj, cond, redisSaveQueue)
resultFlag = append(resultFlag, isSuc)
case iotconst.CONDITION_TYPE_WEATHER:
resultFlag = append(resultFlag, u.WeatherCheck(intellObj, cond, redisSaveQueue))
}
//如果为任意条件满足,同时当前设置条件中已有条件满足,则直接执行
if iotconst.ConditionModel(intellObj.ConditionMode) == iotconst.CONDITION_MODEL_2 &&
resultFlag.EveryOneTrue() {
break
}
}
//根据规则判断条件满足规则
switch iotconst.ConditionModel(intellObj.ConditionMode) {
case iotconst.CONDITION_MODEL_1:
isExecutor = resultFlag.AllTrue() //全部条件满足
case iotconst.CONDITION_MODEL_2:
isExecutor = resultFlag.EveryOneTrue() //任意条件满足
}
最后如果isExecutor=true则开始按照步骤执行任务
在ExecuteTask方法中支持操作设备、延时执行、给手机发送通知、开关某个智能等任务的处理,每个任务都会单独记录日志并反馈给APP用户;
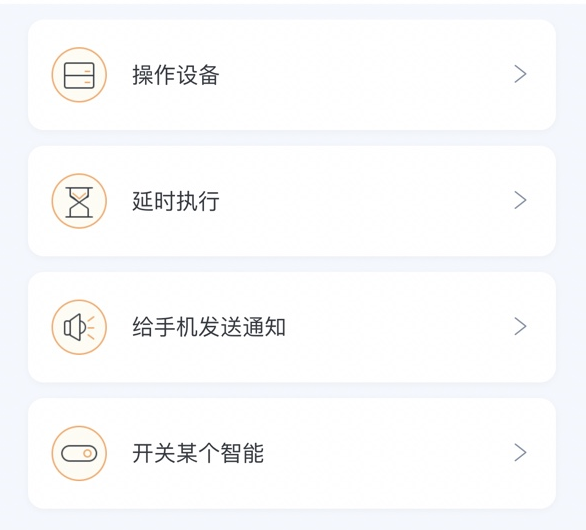
//以下内容为ExecuteTask函数的节选代码
for _, task := range intellObj.SceneIntelligenceTask {
switch iotconst.TaskType(task.TaskType) {
case iotconst.TASK_TYPE_DEVICE:
iotlogger.LogHelper.Info("控制")
setResult(execute.DeviceExecute(userId, resultId, result.RunTime.Unix(), devIds, task))
case iotconst.TASK_TYPE_INTELL:
iotlogger.LogHelper.Info("场景开关")
setResult(execute.SceneIntelligenceExecute(resultId, result.RunTime.Unix(), task))
case iotconst.TASK_TYPE_DELAYED:
iotlogger.LogHelper.Info("延时")
result.RunStatus = 3 //延时执行
execute.SetResult(result)
setResult(execute.DelayedExecute(resultId, result.RunTime.Unix(), task))
case iotconst.TASK_TYPE_SENDMSG:
iotlogger.LogHelper.Info("通知")
setResult(execute.NoticeExecute(execute.NoticeParams{
HomeId: intellObj.HomeId,
UserId: []int64{},
IntelligenceName: intellObj.Title,
AppKey: intellObj.AppKey,
TenantId: intellObj.TenantId,
}, resultId, result.RunTime.Unix(), task))
}
}
以上代码均为代码片段,详细代码可以前往github进行查看哦